


Boron in Glass
Highest boron consumption occurs in the glass industry. When added to the intermediary glass product in molten form, boron enhances the viscosity of the glass and improves the surface hardness and strength of the final product.
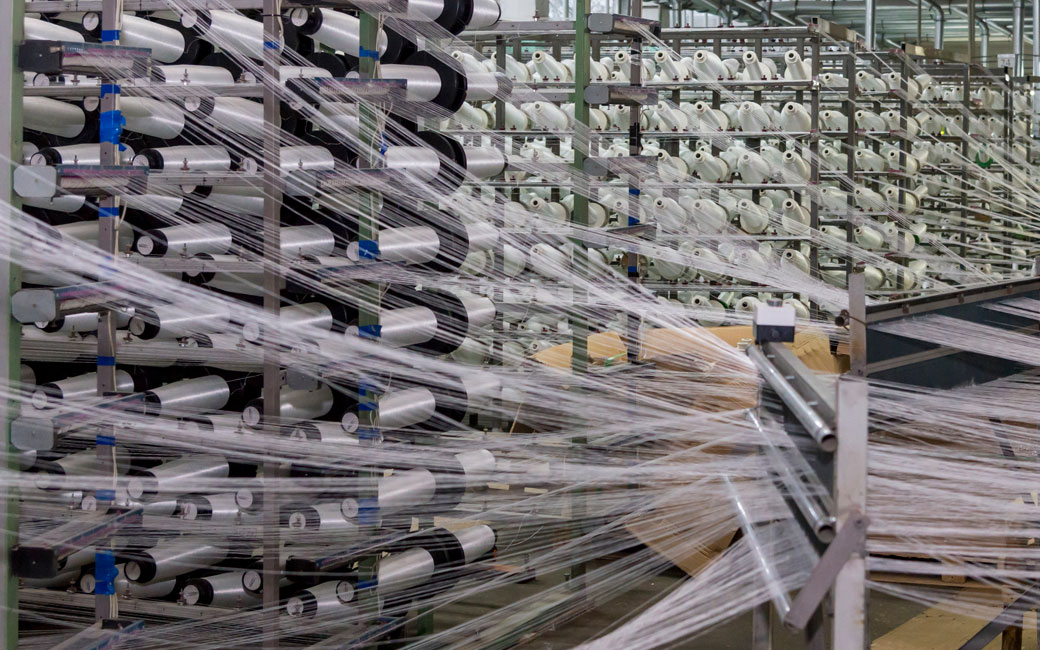
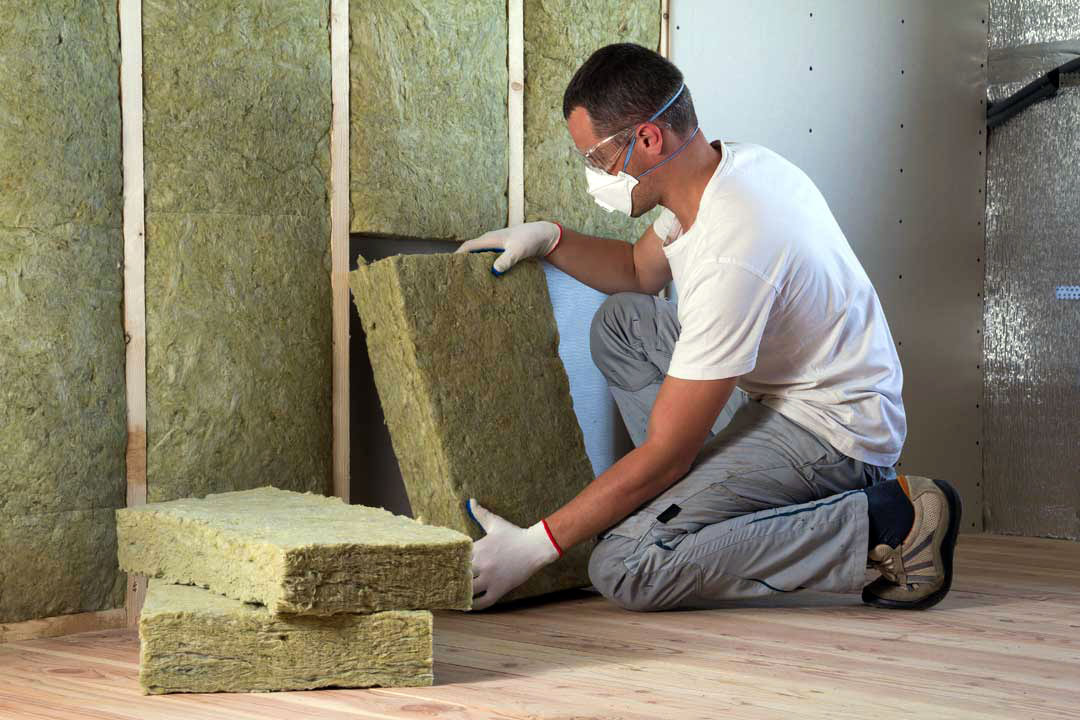
Boron is extensively used primarily in borosilicate glass, textile-type and insulating glass fibers, glass wool, liquid crystal display modules, special furnace containers, laboratory materials, vehicle headlight and signal glasses, LCD (Liquid Crystal Display) monitors and CRT glass products.
Boron is a critical component in the manufacturing of insulation fiber glass, reinforcement fiber glass and borosilicate glass where,
- improves the fluxing capabilities of the batch.
- reduces glass batch melting temperatures.
- increases the fiberising efficiency by lowering the viscosity.
- controls the relationship between temperature, viscosity and surface tension to create optimal glass fiberisation.
- reduces the tendency of crystallisation.
- increases the strength of the fibers against thermal shocks and chemical attacks.